Environment



Environment


Preserving is everyone's duty.
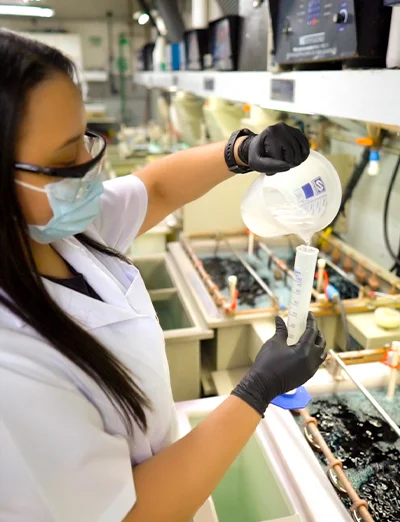
Water on our planet is distributed as follows: 97.5% is salt water found in seas and oceans, and 2.5% is freshwater found in glaciers, rivers, lakes and dams, with only 0.3% available for human use. According to recent studies, with current consumption conditions and misuse of water and if current water resource management conditions are maintained, only a quarter of humanity will have water for their needs by 2050. Besides being essential for the survival of living beings on our planet, water is one of the main raw materials used in the manufacturing process of plated jewelry, acting on a large scale in the cleaning, polishing and washing stages of plated pieces after galvanic processes, where the pieces receive the plating.
It is important to emphasize that after using water in the manufacture of plated pieces, it is no longer suitable for use and becomes a toxic waste, called effluent, which cannot be disposed of in the public sewage collection network.
Given this scenario and concerned about the environmental situation, FC Joias, based on its principles of social responsibility, spares no effort to preserve the environment and has, in its plated manufacturing unit. An Effluent Treatment Station (ETS) responsible for depolluting all water used in the processes mentioned above, complying with the strict criteria and parameters of current environmental legislation in our country. Based on this system we can say, with great pride, that we do not dump any drop of water containing toxic waste into our rivers.
The search for continuous improvement is part of our daily life both with regard to the development of new products, service and everything else that you, our partners, follow throughout our relationship as well as new process technologies. Therefore, we present below two effluent treatment systems adopted in our company for you to learn a little more about us:
Effluent Treatment System
The effluent generated during the surface treatment process of pieces by electrodeposition, generates acidic, alkaline, cyanide effluents, containing heavy metals and for this effluent to return to the environment, it is necessary to be within the standards established by environmental agencies. In this way, the cyanide effluent is treated with sodium hypochlorite at pH 11.5 to 12.8 where cyanides (CN-1) are oxidized to cyanates (CNO-1), which will occur with the consumption of oxygen bound to the oxidizing hypochlorite anion (ClO-1), 1000 times less toxic.
After this stage, the pH is reduced with hydrochloric acid, to 8.0 - 9.5 so that the cyanates are oxidized to carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen (N2). After this process, polymers are added where metals are precipitated in the form of hydroxides.
The precipitate, a pasty residue known as galvanic sludge, is dewatered in a filter press and the resulting cake is placed in drums for disposal in certified companies.
The effluent treatment produces water within the parameters required by environmental control agencies, used for floor washing, toilet flushing or other activities that do not involve human consumption or returned to the urban sewage network.
Ion Exchange System
With the use of this system, all water used in part of the plating process of plated pieces is purified, making it suitable for industrial use, causing a reduction in water consumption and, consequently, a decrease in the amount of chemical products needed for waste treatment.

Contact us.
Request personalized service.